How Do Generators Work Without Electricity?

We all need electricity to run our daily activities and business operations, but power outages can sometimes be inevitable. Luckily, generators are here to provide us with electrical energy during the times when we need it the most.
But how do generators work without electricity? You will know all the answers right here, so keep reading!
How Does a Generator Work?
Whether you’re at home or in the office, generators are used to power everything from lights and appliances to air conditioners and refrigerators. But how exactly do they work?
Generators produce electricity by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy through the use of magnets and coils of wire. These magnets and coils work together to create an electromagnetic field between them.
The mechanical energy is usually provided by a prime mover, which can be an electric motor or steam turbine. A generator is a rotating machine that contains coils of wire that move as the magnetic field inside the generator changes direction.
As these coils move in response to changes in the magnetic field and produce electric current, they produce alternating current (AC).
There are several different types of engines used in generators, including gasoline and natural gas engines. When you’re looking at different models of generators, it helps to know what kind of fuel they require so that you can find one that will work well for your unique needs.
What Are the Parts of a Generator?
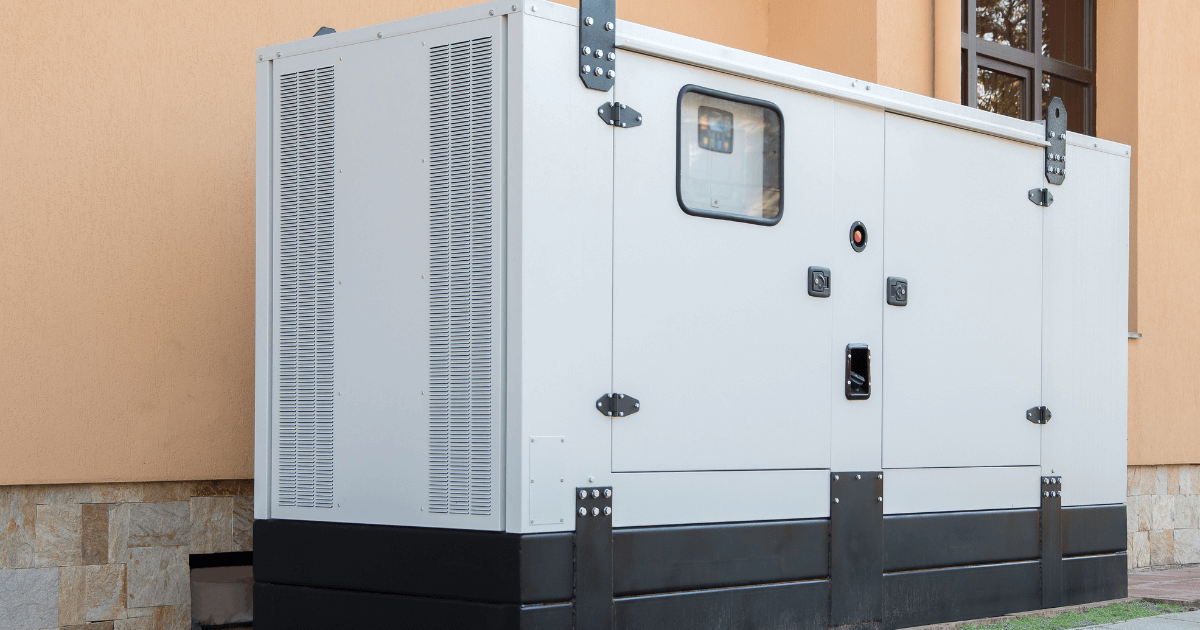
The parts of a generator can be divided into two main categories: the prime mover, which provides the mechanical energy, and the electrical components, which convert the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The prime mover is the source of the mechanical energy that drives the generator. This can be a gasoline or diesel engine, a steam or water turbine, or any other source of mechanical energy.
The electrical components of a generator include the following:
- Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the generator that consists of a set of windings or coils.
- Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the generator that is connected to the prime mover. It contains a set of windings or coils that are positioned near the stator.
- Field winding: The field winding is a set of windings or coils that are used to produce the magnetic field in the generator.
- Exciter: The exciter is a small generator that is used to supply the field current to the field winding of the main generator.
- Voltage regulator: The voltage regulator is a device that is used to control the output voltage of the generator. When the generator runs below its maximum operating level, the voltage regulator begins the cycle of converting AC current to AC voltage to maintain the normal operating capacity.
- Bearings: The bearings are used to support the rotor and allow it to rotate smoothly.
- Cooling system: The cooling system is used to keep the generator components cool during operation.
- Enclosure: The enclosure is a casing that protects the generator from the environment and provides a mounting place for the various components.
- Control panel: A control panel is a group of switches, gauges, and other components that are used to start, stop, and control the operation of the generator.
- Battery charger: A battery charger keeps a generator ready to use if needed. It keeps the battery of the generator charged by providing float voltage.
What Are the Types of Generators?
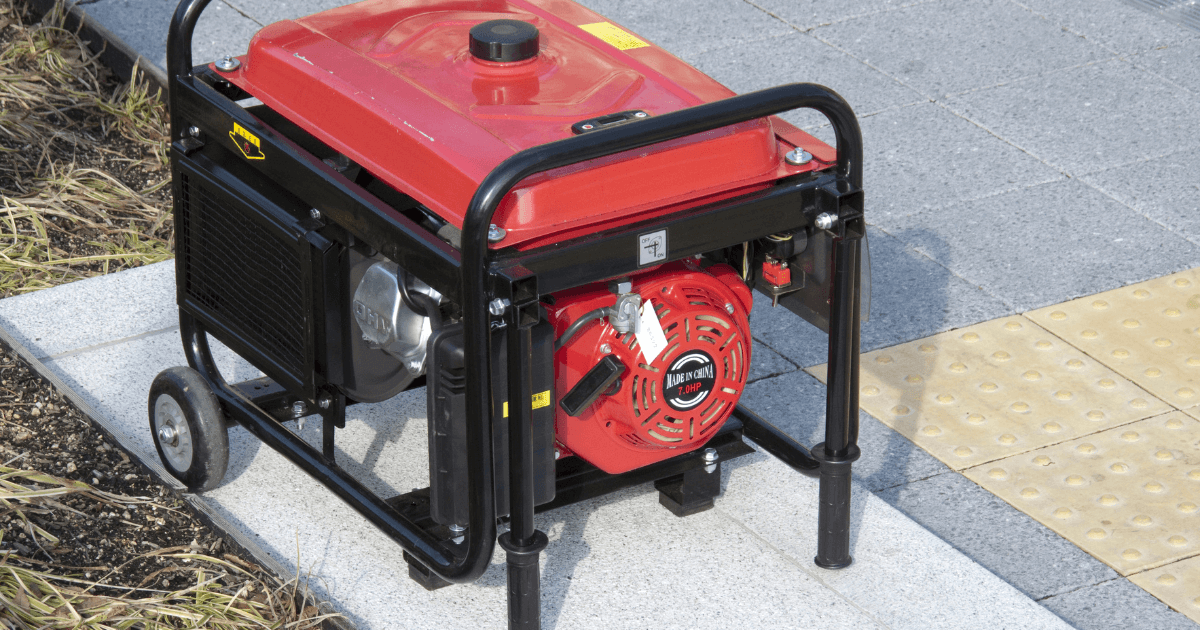

Portable Generator
A portable generator is a small, portable unit that can be used to power a variety of electrical devices. They are typically powered by gasoline and are used for backup power or recreational purposes.
Standby Generators
Standby generators are larger units that are installed permanently in a home or business. They are typically powered by natural gas or propane and are designed to automatically turn on in case of a power outage.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are portable units that use an inverter to produce a stable, clean power supply that is suitable for sensitive electronic devices. They are typically smaller and produce less operating noise than other types of generators.
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators are powered by a diesel fuel system and are used for backup power or in areas where there is no access to the power grid. It comes with a fuel system that is attached to an external fuel tank to supply diesel fuel to the generator unit. They are typically larger and more powerful than other types of generators.
Expertise and Experience
Gas Turbine Generators
Gas turbine generators are powered by a gas turbine and are used to produce electricity on a large scale. These generators often use natural gas, kerosene, propane, or jet fuel. They are often used in power plants and industrial settings.
Steam Turbine Generators
Steam turbine generators use steam to turn a turbine, which in turn generates electricity. They are often used in power plants and industrial settings, just like gas turbine generators.
Microgrid Generators
Microgrid generators are small-scale power generation systems that can operate independently or in conjunction with the power grid. They are often used in remote or off-grid locations to produce electricity.
How Long Do Generators Last?
The average generator’s lifespan is between five and ten years. As a rule of thumb, generators that are frequently used may require more frequent repairs or replacements, compared to those that are less frequently used.
These estimates, however, are all dependent on proper and regular generator maintenance.
Get Professional Help to Install Generators
If you’re looking for a fast and reliable electrician in Prescott, Arizona, our technicians at Assurance Electrical Services are more than happy to help! When it comes to installation, maintenance, or repair of generators and other electrical issues, our team can ensure to address your electrical needs. Call us today at (928)713-2177.
